Chava Rosenfarb
Chava Rosenfarb, a major Yiddish novelist of the second half of the twentieth century, is one of the few Holocaust survivors who transmuted their experiences into fiction rather than memoirs or reminiscences.

Fanny "Bobbie" Rosenfeld
Käte Rosenheim
A social worker by training, Käte Rosenheim held numerous public service positions in Germany before the Nazis took power. In 1933 she joined the Reich Representation of German Jews; before she herself fled to the United States in 1940, she facilitated the escape of over 7,250 Jewish children from Nazi Germany.

Hadassah Rosensaft
Dr. Hadassah Bimko Rosensaft played an instrumental role in saving the lives of fellow concentration camp inmates at Auschwitz-Birkenau and then at Bergen-Belsen. Rosensaft was later involved in the creation of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.

Etta Lasker Rosensohn
An influential philanthropist and social activist, Etta Lasker Rosensohn focused most of her energy on Jewish and Zionist affairs in New York City. Her great passion was Hadassah, where she served on the national board for more than two decades and as the national president.

Nettie Rosenstein

Doris Rosenthal
Henrietta Rosenthal

Ida Cohen Rosenthal
Ida Cohen Rosenthal not only created the modern bra, she also helped found Maidenform, Inc., and make it the most successful bra manufacturer in the world.

Jean Rosenthal
Jean Rosenthal was a pioneer in theater lighting design, finding new aesthetics for dance performances and theater productions. Rosenthal did the stage lighting for a number of well-known Broadway plays and musicals, such as West Side Story (1957), Becket (1960), Hello, Dolly! (1964), Hamlet (1964), Fiddler on the Roof (1964), The Odd Couple (1965), and Cabaret (1966). She is most famous for her unconventional lighting of dance and opera performances.

Frances Rosenthal Kallison
Frances Elaine Rosenthal Kallison was a horsewoman and historian, a cofounder of the Texas Jewish Historical Society, and the only Jewish woman in the National Museum and Cowgirl Hall of Fame. A regional leader of the National Council of Jewish Women, she lobbied to end the poll tax and open pre-natal clinics for the poor. The exhibit she curated on Texas Jewry for the 1968 World’s Fair in San Antonio has been continually updated.
Esther Rosenthal-Shneiderman

Julie Rosewald
Julie Eichberg Rosewald was America’s first woman cantor. Known as the “Cantor Soprano” at Temple Emanu-El in San Francisco, she served between 1884 and 1893. Rosewald enjoyed a brilliantly successful career in opera as well as being a composer, author, teacher, and professor of music.

Betty Ross
Betty Ross was a journalist known for her international purview and interviews with celebrities. In the mid-1920s she traveled extensively through Asia, Europe, the Middle East, and Russia, gathering materials and interviewing celebrities. She was among the first journalists to conduct radio interviews.

Mattie Rotenberg
The first woman and the first Jew to be granted a doctorate in physics at the University of Toronto, Mattie Rotenberg also founded Toronto’s first Jewish day school in 1929 to educate her five children. She went on to embark upon a successful second career in journalism.

Joan Roth
Born in Detroit, Joan Roth has worked with many well-known photographers in her long career and is primarily interested in photographing Jewish women. In 1983, Roth joined the rescue missions airlifting Ethiopian Jews to Israel. Inspired by the photographs she took there, Roth traveled to Jewish communities all over the world photographing Jewish women in rapidly disappearing communities.

Lillian Roth
Lillian Roth, a singer-actor whose career met with early success but was eventually sidetracked by alcoholism and mental illness, wrote an autobiography that became an international bestseller. At fourteen Roth landed a part in the Shubert show Artists and Models; by seventeen, she was in Ziegfield’s Midnight Follies. She moved to Hollywood for a successful film career before her life fell apart due to mental health challenges and alcoholism.

Martine Rothblatt

Sylvia Rosner Rothchild
Sylvia Rosner Rothchild was a prolific writer and historian whose works of fiction and nonfiction explored American Jewish identities and captured audiences. Many of her writings depict the descendants of Eastern European Jews who arrived in the United States in the decades surrounding the turn of the twentieth century.
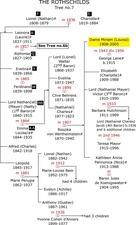
Rothschild Women
The Rothschild family expanded from the mid-1700s to the present day. The women of the family were known for being leaders in philanthropy and business, as well as exceptional hostesses.

Baroness Germaine de Rothschild
A member of one of France’s most privileged Jewish families, Germaine de Rothschild (née Halphen) was a noted philanthropist, accomplished musician, author of two books, and mother of four. Most significantly, she orchestrated France’s Kindertransport efforts, helping provide refuge to between 350 and 450 Jewish children.

Bethsabée Rothschild
Bethsabée (Hebrew: Batsheva) de Rothschild, the scion of a well-known philanthropic family, helped support numerous activities in the United States and Israel, especially dance, music, and science.She created the Batsheva and Bat-Dor dance companies and was awarded the Israel Prize in 1989 for her special contribution to Israeli society.

Dame Miriam Rothschild
Dame Miriam Rothschild was a renowned British natural scientist who published over 300 scientific papers throughout her lifetime, making groundbreaking contributions to the fields of entomology, zoology, marine biology, and wildlife conservationism. In 1985 she was made a Fellow of the Royal Society and credited for her work in the histology, morphology, and taxonomy of fleas.

Hannah de Rothschild, Countess of Rosebery
A member of the English Rothschild family who married the Earl of Rosebery, a future Prime Minister of England, Hannah was a devoted wife, mother, and philanthropist.

Lady Louise Rothschild
Lady Louise Rothschild came from a distinguished line of Anglo-Jewish aristocracy. Using her unrivaled social status, she founded the first independent Jewish women’s philanthropic associations in 1840, inspiring upper- and middle-class Anglo-Jewish women to venture outside the home and into public life for the first time.


