Family: Motherhood

Henriette Fürth

Abraham Geiger
Abraham Geiger (1810-1874) was one of the most influential Jewish thinkers of the nineteenth century. He was one of the major intellectual leaders and founders of the Reform movement in Germany and a strong supporter of Jews entering European society. As part of his vision of Judaism, he argued for a Judaism oriented around the home and domestic life, but also a Judaism that both elevated and sidelined the women that had long created that domestic life.

Germany: 1750-1945
The Jewish Reform movement did not liberate women from their subordinate religious status, and the nineteenth-century bourgeois German family ideal with its rigid gender roles soon eclipsed the fluid structure of premodern Jewish families. Jewish women were expected to transmit German bourgeois values while also shaping their children’s Jewish identity.

Louise Glück
Louise Glück, American poet, essayist, and educator, was the recipient of the 2020 Nobel Prize in Literature, as well as numerous other awards for her writing; she also served as poet laureate of the United States from 2003 to 2004. One finds the personal, the mythological, and the Biblical woven intricately throughout Glück’s oeuvre.

Glueckel of Hameln
Born into an affluent family in Hamburg, Glückel of Hameln became the business partner of her beloved first husband. She began writing memoirs in 1691, after her husband’s death. These memoirs are incredibly detailed, combining a meticulous record of her life and descriptions of events that occurred in local Jewish communities. Her memoirs are both a singularly important social and historical document and one of the greatest literary achievements of Ashkenazi prose–in Yiddish or Hebrew–at least until the end of the eighteenth century.

Judy Gold

Hadassah: Yishuv to the Present Day
Hadassah, the Women’s Zionist Organization of America (HWZOA) has a lengthy history of activity in the Yishuv and Israel, going back to 1913, about a year after it was founded in New York, and continuing to this day. This activity, outstanding in its scope, continuity, stability, and diversity, encompasses efforts in the sphere of health and medical services and in the welfare of children and youth.

Haganah
Women played many different roles in the operations of the Haganah. Though their stories are frequently excluded from the story of the Jewish paramilitary organization in British Mandate Palestine, women served as caretakers and nurses, as well as fighters and commanders.
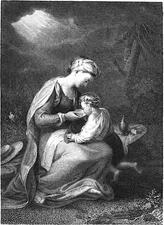
Hagar: Bible
Hagar is Sarah’s Egyptian slave woman, whom Sarah gives to Abraham as secondary wife and who would bear a child for him. After Hagar becomes pregnant, Sarah treats her harshly. Eventually Hagar flees from her mistress into the wilderness, where God’s messenger speaks to her. Hagar has long represented the plight of the foreigner, the slave, and the sexually abused woman.

Hagar: Midrash and Aggadah
Hagar is the subject of much interpretation by the rabbis, who portray her as a spiritual and even righteous woman. The rabbis often depict her relationship with Sarah as harmful and fractious, though some traditions identify her with Keturah, taken as a wife by Abraham in Gen. 25:1; in this interpretation, after their divorce she remarried Abraham after Sarah’s death.
Julia Horn Hamburger
A long-time volunteer, Julia Horn Hamburger was founding president of the New York Children’s Welfare League, which offered health and education services to immigrant children, the founding vice president of the Jewish Theater for Children and founding president of Ivriah, the women’s division of the Jewish Education Association. During WWII she shifted her focus to aiding the American Jewish Committee and the Anti-Nazi League.
Hamutal: Bible
Hamutal was one of the queens of the Kingdom of Judah and had a great deal of influence over her sons’ reigns.

Hannah Mother of Seven
The mother of seven is a nameless figure from II Maccabees who was arrested and died along with her seven sons for defying the decree of the Seleucid monarch to transgress the commandments of the Torah. Her death is retold in rabbinic and medieval literature, where she is named both Miriam and Hannah.

Hannah: Bible
Hannah, the second and barren yet preferred wife of Elkanah, promises to return her child to YHWH if he grants her a son. Her prayers are answered, and she follows through on her pledge to YHWH. Hannah’s narrative emphasizes the importance of fertility and childbirth in Israeli artistic narratives and presents a portrayal of an independent and resourceful woman.

Hannah: Midrash and Aggadah
Hannah is depicted by the Rabbis as a righteous woman who was devout in her observance of the commandments and tested by God through her infertility. Her story is the basis for much of the rabbinic conception and rules of prayer.
Hasidic Hebrew Fiction: Portrayal of Women
Hundreds of compilations of Hasidic literature, a genre derived from oral traditions, were published in Eastern Europe between the start of the nineteenth century and the outbreak of World War II. The image of “woman” varies in Hasidic literature according to the character in the story, its narrator, and its setting in time and place; therefore we can only refer to individual women, each on her own, and not to woman in general or women as a gender.

Haskalah Attitudes Toward Women
Just as the many well-known thinkers of the Enlightenment debated the proper role of women in society, so did the maskilim, the men of intellect who burst upon Ashkenazi Jewish society in the eighteenth- and nineteenth-century revolution known as Haskalah. Dominated by men, the movement critiqued Jewish tradition and encouraged modernity among Jews, but simultaneously met Jewish women’s pursuit of modernity with ambivalence.
Haskalah Literature: Portrayal of Women
The image of women in Haskalah literature reflects the relationship between the sexes in eighteenth- and nineteenth-century Ashkenazi Jewish society and European culture. But Haskalah writers wished to shape new patterns of male-female relationships among their reading public; to change, at least partly, the attitude of men towards women; and to ‘improve’ women’s conduct within the home and community.

Hasmonean Women
Though few of their names were documented, the women of the Hasmonean family were important figures in political and familial affairs during the second and first centuries BCE.

Hebrew Women in Egypt: Bible
Hebrew women in Egypt are critical figures in the Bible, especially concerning their maternal and physically nurturing roles. Hebrew midwives help male babies escape the infanticide commanded by the Pharaoh, and another woman helps save baby Moses’ life. These stories show how women were able to undermine the Pharaonic authority and ensure the survival of the Hebrew people in general.

Hebrew Women in Egypt: Midrash and Aggadah
The Rabbis famously maintain that the Israelites were redeemed from Egypt by merit of the righteous women of that generation, who strove mightily to continue to bring forth children, regardless of the grueling servitude and despite Pharaoh’s decree that the male children be killed.
Holocaust Literature
Literature by and about women and the Holocaust explores the impact of the Nazi genocide on women during and after the war, its impact on subsequent generations, and the reflections of women on the implications of the Holocaust. Encompassing a range of literary genres, including fiction, poetry, drama and memoir, women’s Holocaust writing explores the intersection of history, imagination, Jewishness and gender.
Holocaust Survivors: Rescue and Resettlement in the United States

Rebekah Gumpert Hyneman
Rebekah Gumpert Hyneman was one of a small group of American Jewish women who published their work in the nineteenth century. She used her writing to showcase her love and devotion to Judaism. In her work, she encouraged American Jews to resist assimilation and understand the significance of their religion and also aimed to educate uninformed and anti-semitic non-Jews.


